Mumbai: JSW Steel Limited (“JSW Steel” or the “Company”) today reported its financial results for the Third Quarter ended 31st December 2025 (“Q3 FY26” or the “Quarter”).
The global economy has continued to grow steadily despite tariffs and geopolitical challenges. The IMF has raised its 2026 growth forecast by 20bps to 3.3% while keeping its 2027 outlook unchanged at 3.2%. Market sentiment has been buoyed by trade deals and resilient economic data in developed markets. Supportive policies, easing financial conditions and AI related investments are providing further growth momentum. However, recent developments have raised concerns regarding tariffs again, and need to be monitored.
In the United States, technology related investments and robust consumer spending provided strong growth momentum in 2025. The impact of tariffs on inflation and growth has been limited, however, there could be risks from a lagged effect. Growth momentum in China decelerated in the second half of 2025 due to continued contraction in the real estate sector, although manufacturing and exports showed positive growth. In 2026, China’s growth should be helped by favorable fiscal and monetary policies along with ongoing consumption subsidies and anti-involution measures.
India continues to lead global growth among major economies. Advance estimates peg FY26 GDP growth at 7.4%, supported by strong domestic demand, steady Government capex, and supportive monetary and financial conditions. The Indian government imposed anti-dumping duty on HRC from Vietnam in November and CRNO electrical steel from China in December 2025. The Safeguard Duty was formalised for 3 years in December, in-line with the DGTR recommendations. During Q3 FY26 India’s finished steel consumption grew by 4.6% YoY to 40.74mt, while crude steel production rose by 10.0% YoY to 42.50mt. During the quarter, steel imports fell by 42.4% YoY while exports grew 35.5% YoY. China’s steel production declined by 4.4% YoY to 961mt in CY 2025, but exports surged 14% YoY to 133.5mt (including semi-finished steel) during the year.
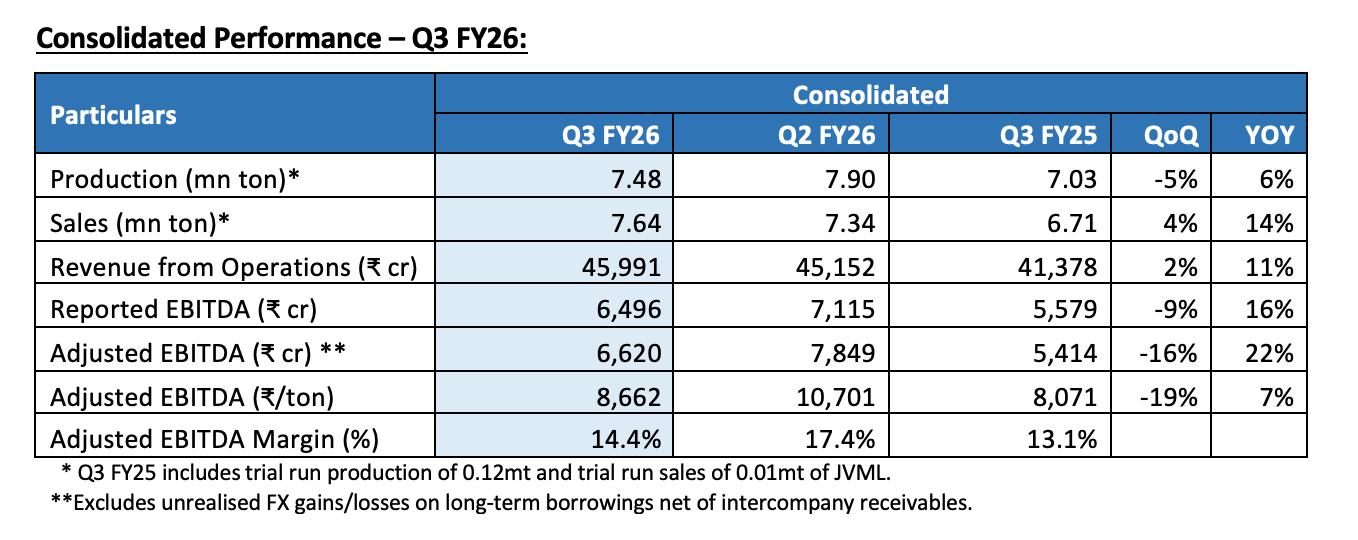
Consolidated Crude Steel Production for Q3 FY26 was 7.48 million tonnes, up 6% YoY driven by the ramp-up of the JVML-Vijayanagar project; however, production fell 5% QoQ due to shutdown of Blast Furnace-3 (BF-3) at Vijayanagar from the end of September 2025 for upgradation of capacity.
Consolidated Sales were highest ever at 7.64 million tonnes, up 14% YoY on the back of healthy domestic demand. Domestic sales stood at 6.59 million tonnes, reflecting an increase of 10% YoY. Exports at 0.84 million tonnes, increased by 53% YoY, contributing 11% to the sales from the Indian operations for Q3 FY26. Retail sales volumes were up 12% YoY.
The Company registered Revenue from Operations of ₹45,991 crores and Adjusted EBITDA of ₹6,620 crores, with a margin of 14.4%. The Adjusted EBITDA increased by 22% YoY, driven primarily by higher volumes and lower coking coal and power costs, partly offset by lower realisations. Reported EBITDA was ₹6,496 crores during the quarter.
The Adjusted EBITDA excludes unrealised forex gains and losses on long-term borrowings, net of unrealised forex gains and losses on intercompany receivables. The Adjusted Operating EBITDA better reflects our operating performance.
Profit after Tax for the Quarter stood at ₹2,410 crores after recognising deferred tax assets (net) amounting to ₹1,439 crores on the brought forward unabsorbed depreciation in Bhushan Power & Steel Limited (“BPSL”) as it is probable that carried forward unabsorbed depreciation will be recovered against the likely capital gains on the slump sale of BPSL’s steel business undertaking.
The Company’s Net Gearing (Net Debt to Equity) stood at 0.92x at the end of the Quarter, as against 0.93x at the end of Q2 FY26, and Net Debt to EBITDA stood at 2.91x, as against 2.97x at the end of Q2 FY26. Net Debt as of 31st Dec 2025 stood at ₹80,347 crores.
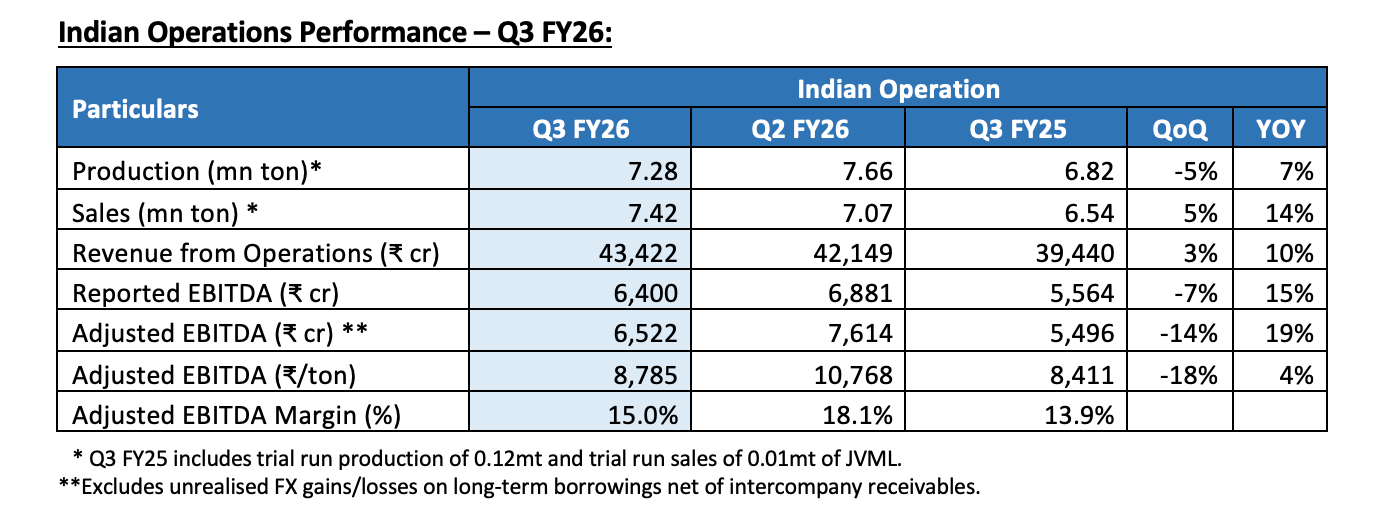
Crude Steel Production at the Indian Operations for the Quarter was 7.28 million tonnes, up 7% YoY. The capacity utilisation for Indian operations for the quarter was at ~93% excluding BF-3 capacity at Vijayanagar which is under shutdown, and was at 85% including BF-3 capacity.
Steel Sales for the Quarter was the highest ever at 7.42 million tonnes, higher by 14% YoY. During the quarter the company reduced steel product inventories by ~0.3 million tonnes.
The Indian Operations registered Revenue from Operations of ₹43,422 crores. Adjusted Operating EBITDA was ₹6,522 crores, higher by 19% YoY. The Adjusted Operating EBITDA per tonne was ₹8,785 and margin for the Quarter was 15.0%. Adjusted EBITDA was lower YoY mainly due to lower realisations and higher coking coal cost. Reported Operating EBITDA was ₹6,400 crores for the Quarter.
Profit after Tax was ₹2,668 crores for the Quarter.
Standalone Performance – Q3 FY26:
Crude Steel Production for the Quarter was 5.08 million tonnes, lower by 11% YoY and 13% QoQ. Steel Sales for the Quarter was 5.55 million tonnes, lower by 1% YoY and 5% QoQ.
The Company registered Revenue from Operations of ₹32,127 crores, higher by 1% YoY. Adjusted EBITDA was at ₹4,227 crores for Q3 FY26, lower by 3% YoY and 23% QoQ. The EBITDA margin for the Quarter was 13.2%. Reported EBITDA was ₹4,121 crores for the Quarter.
The Company reported Profit after Tax of ₹757 crores for the Quarter.
Performance of Subsidiaries – Q3 FY26:
Bhushan Power & Steel Ltd (BPSL):
During the quarter, BPSL registered Crude Steel Production of 1.0 million tonnes and Sales volume of 0.98 million tonnes. Revenue from Operations and Adjusted EBITDA for the quarter stood at ₹5,770 crores and ₹611 crores, respectively. The Adjusted EBITDA declined by 16% QoQ, primarily due to lower realisations and higher coking coal cost. BPSL reported a Profit after Tax of ₹1,578 crores for the quarter.
JSW Vijayanagar Metallics Ltd (JVML), Vijayanagar:
During the quarter JVML reported Crude Steel Production of 1.18 million tonnes, reaching the rated capacity after commissioning all balance facilities in Q2 FY26. Sales volume for the quarter was 1.23 million tonnes. Revenue from Operations and Adjusted EBITDA for the quarter stood at ₹6,099 crores and ₹921 crores, respectively. The Adjusted EBITDA increased by 47% QoQ, mainly driven by higher volumes. JVML reported a Profit after Tax of ₹382 crores for the Quarter.
JSW Steel Coated Products Ltd:
During the quarter, JSW Steel Coated Products registered a production volume (GI/GL, Tin, CRCA & other saleable products) of 1.16 million tonnes and sales volume of 1.18 million tonnes. Revenue from Operations for the quarter stood at ₹8,776 crores, and Adjusted EBITDA was ₹532 crores. The Adjusted EBITDA was lower QoQ, primarily due to lower sales realisations and the impact on inventory due to fall in HRC prices. The subsidiary reported a net profit of ₹178 crores for the quarter.
USA – Ohio:
The EAF-based steel manufacturing facility in Ohio, USA, produced 219,197 net tonnes of Slabs during the quarter. Capacity utilisation was at 61% during the quarter. Production was lower due to scheduled outage for caster upgrades from 15th December 2025 to 11th January 2026. Sales volume for the quarter stood at 1,88,837 net tonnes of Slabs and 52,391 net tonnes of HRC. It reported an EBITDA of US$ 0.20 million for the quarter.
USA – Plate & Pipe Mill:
The Plate & Pipe Mill based in Texas, USA produced 122,981 net tonnes of Plates and 15,647 net tonnes of Pipes, reporting a capacity utilization of 52% and 11%, respectively, during the quarter. Sales volumes for the quarter stood at 1,08,387 net tonnes of Plates and 8,446 net tonnes of Pipes. It reported an EBITDA of US$ 2.87 million for the quarter, lower QoQ primarily due to lower sales volumes and realisations for Plates.
Italy Operations:
The Italy based long products manufacturing facility produced 77,051 tonnes and sold 78,537 tonnes of rolled products and grinding balls during the quarter. It reported an EBITDA of €5.25 million for the quarter, marginally lower QoQ due to lower sales volume.
Update on Projects:
The JVML-Vijayanagar project was fully commissioned and the plant has ramped up to full capacity during Q3. The Blast Furnace-3 in Vijayanagar was shut down in end-September 2025 for upgradation and expansion from 3.0 MTPA to 4.5 MTPA. The blast furnace will be commissioned by the end of Q4 FY26.
At the Dolvi Phase-III expansion from 10 MTPA to 15 MTPA, long lead time items have been ordered and letters of credit established. The project will be completed by September 2027.
At the Kadapa 1 MTPA EAF and Structural mill project, technical and commercial discussions for equipment are underway. The project is expected to be commissioned by FY29.
The Board has approved a 5 MTPA steel plant at our new site in Jagatsinghpur, Odisha. The project will be housed in our subsidiary, JSW Utkal Steel Ltd., and will entail a capex of ₹ 31,600 crores with commissioning by FY30. This project is the first phase with expansion potential to 13.2 MTPA at this site. We had already commenced setting up two 8 MTPA pellet plants at Jagatsinghpur, and a 30 MTPA slurry pipeline to transfer iron ore from our mines to this plant. The two pellet plants are expected to be commissioned by FY28. The construction of the slurry pipeline, being set up by JSW Infrastructure Ltd., is progressing well and expected to be commissioned in FY27.
In line with our strategy to enhance our downstream capabilities to address market requirements, the board has approved a 0.2 MTPA Tinplate and 0.36 MTPA Continuous Galvanising Line at our existing downstream plant in Rajpura, Punjab.
The Company’s consolidated capex spend during Q3 FY26 was ₹3,482 crores, and ₹10,018 crores during 9M FY26. We expect to spend ₹15,000-16,000 crores during FY26.
Energy Transition
In line with the Company’s energy transition goals, the Board had approved 2.5 GW of renewable energy and 320 MWh of battery storage capacity. 1 GW of renewable power capacity has been commissioned as of Q3 FY26. The company successfully commissioned India’s first Diesel-to-Battery converted locomotive at Vijayanagar during the quarter.
Strategic Joint Venture for BPSL
On 3rd December 2025, the Company announced a strategic JV with JFE Steel, Japan, for its BPSL steel business. With this transaction, JFE will take a 50% stake in the BPSL Steel business at an equity value of ₹31,500 crores and enterprise value of ₹53,000 crores. This transaction will enable a cash inflow of ₹32,000 crores and a substantial deleveraging of ₹37,000 crores for JSW Steel. This partnership allows us to grow the BPSL business through capacity expansion and JFE Steel’s technological strength. It also allows JSW Steel to accelerate growth across its portfolio in a financially prudent manner to meet India’s growing steel demand.
Outlook
The global economy continues to hold steady, with the IMF slightly raising its 2026 growth forecast to 3.3% similar to its growth estimate for 2025. Despite ongoing trade policy and geopolitical headwinds, momentum is being supported by strong tailwinds from AI and technology investments, particularly across North America and Asia. Overall, growth is also getting a further lift from supportive policies, easy financial conditions, and the private sector’s ability to adapt quickly.
In the U.S., growth remains strong heading into CY26, supported by a surge in tech‑related investments and continued resilience in consumer spending, even as the labour market shows signs of gradual cooling. Following 75 bps of rate cuts in 2025, some additional policy easing is expected in the year ahead. The impact of tariff measures on inflation and growth has so far been limited, though the risk of lagged effects persists.
The Eurozone economy is in a phase of modest expansion, led primarily by Services, even as Manufacturing remains comparatively weak. Policy rates are currently on hold, with inflation hovering near target and growth expectations revised upward. Expansionary fiscal policies are expected to provide medium‑term support, particularly to manufacturing.
In China, growth momentum softened in H2CY25, driven by weak FAI and continued contraction in the real estate sector. However, Manufacturing and exports recorded positive growth, offering some offset to broader domestic softness. Fiscal and monetary policies are expected to remain growth‑supportive in 2026, with a continued focus on consumption subsidies, targeted stimulus, and anti‑involution measures aimed at improving business productivity and household confidence.
India’s outlook remains strong, supported by GST rationalisation, supportive monetary policy, benign inflation and robust government capex. NSO placed its advance estimate for FY26 GDP growth at 7.4% and both RBI and IMF have revised their forecasts upward. Domestic demand remains healthy, with double‑digit auto sales growth in Q3FY26 and improving discretionary consumption.
Rural indicators are also firm, supported by strong tractor and 2W sales, higher kharif output, robust rabi sowing, and lower MNREGA demand. Central government capex remains on track, rising 28% in Apr–Nov’25 despite easing in Oct–Nov.
Commercial real estate trends are robust, though residential sales have been modest recently. Conditions for private capex are improving, aided by better capacity utilization and stronger balance sheets.
Recent acceleration of economic reforms and trade agreements by India bode well for the medium-term growth prospects, strengthening India’s resilience amid global challenges.









